Indianz.Com > News > Gaylord News: Tribes being forced out of homelands is key part of U.S. history
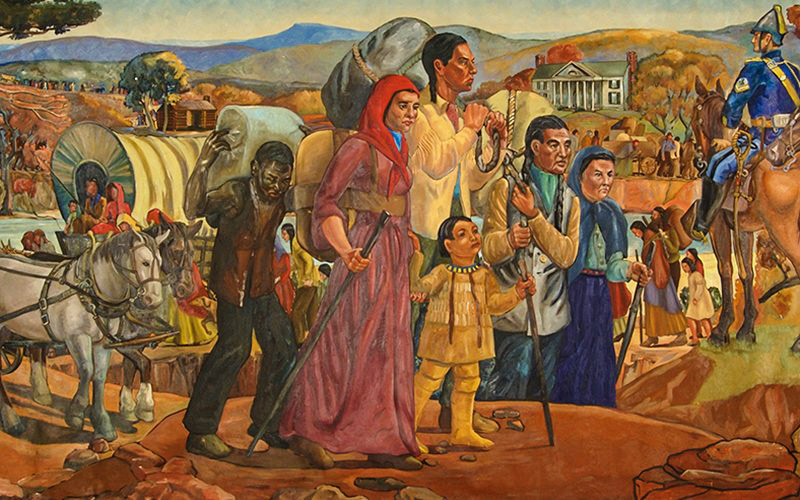
Cherokee Trail of Tears just one of many forced removals of Eastern tribes to Oklahoma
Monday, January 11, 2021
Gaylord News
WASHINGTON – The Trail of Tears, the forced removal of the Cherokee Nation to Oklahoma, was one of the most inhumane policies in American history – but it wasn’t an isolated incident.
In 1831, nearly 16,000 members of the Cherokee Nation were forced under armed guard to leave their native lands in the southeastern United States to trek more than 1,000 miles to what eventually would become the state of Oklahoma.
Almost 4,000 Cherokees died along the way, never making it to the land designated by the U.S. government as Indian Territory.
Removal of the Choctaw Nation began even earlier, in 1830. Like the Cherokees, they were forced to leave their homes in the South and a way of life developed over millennia to start over in an alien environment on the prairie.
But the Cherokee and Choctaw nations are only two of the tribes with a removal story. There are 39 tribes in Oklahoma, five native to the state, that have stories to be told – each with its own trail of tears.



‘On the far end of the Trail of Tears’: On July 8, 2020, the U.S. Supreme Court held that the reservation promised to the Muscogee (Creek) Nation by treaty was never diminished by Congress.
This year marked the 50th anniversary of President Richard Nixon’s speech advocating for Indian self-determination. “They kept taking and taking and taking. It was only in the 1970s that the tribes really began to reverse all of that,” Gover said. “We’ve been in what we call a self-determination era only for the last 50 years.” Despite these challenges, Cole said, tribes are responsible for much of the economic growth in the state, especially in rural communities. Oklahoma tribes had a $12.9 billion impact on the state’s economy in 2017, making them one of the top economic drivers, according to a study on Oklahoma Native Impact. “Oklahoma tribes support 96,177 jobs in the state, representing $4.6 billion in wages and benefits to Oklahoma workers. While direct employment exceeds 50,000 jobs, tribal investment spurs job growth in many different industries,” the report said. If Native communities were to leave Oklahoma, Gover said, many non-Indians who depend on the tribes would suffer. To understand the accomplishments and cultures of tribal nations today requires understanding the merciless removal period, he said. “The only thing I’m confident about is that the Indians will never give up,” Gover said, “and they will never stop being Indians.”
The Muscogee Treaty of 1790 > now on display as part of #NationToNation exhibition #HonorTheTreaties pic.twitter.com/IJvQC3Xo2s
— National Museum of the American Indian (@SmithsonianNMAI) March 16, 2015
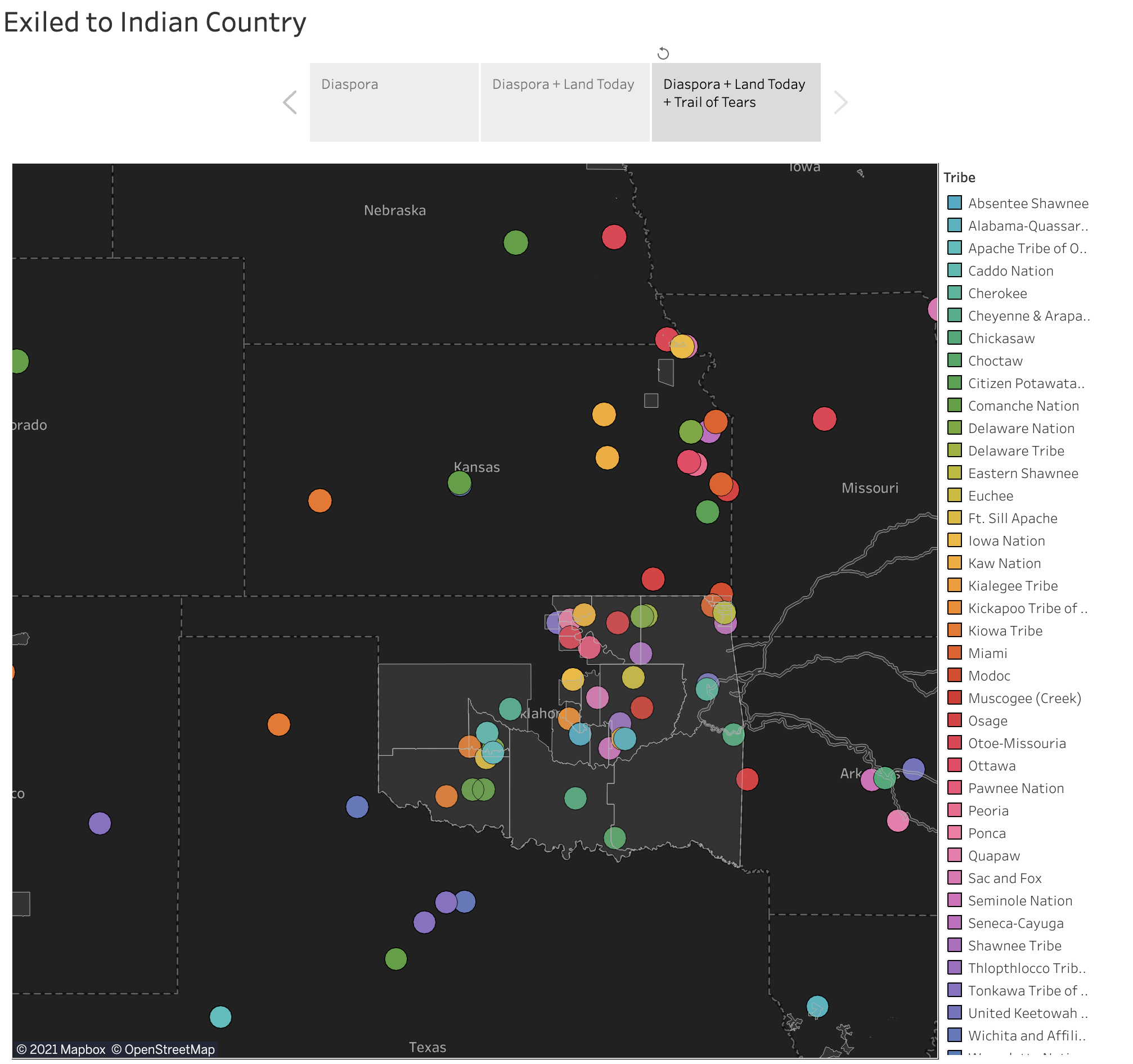
Visualize the diaspora
These maps
visualize the forced diaspora of the 39 recognized tribes of Oklahoma across centuries. It is intended to indicate locations or areas in or around which a tribe has lived, presently lives, and/or has at some point been significant to that tribe’s history.
Click on any one coordinate to see other coordinates that indicate places associated with a given tribe or select any tribe on the sidebar to see the same effect. Navigate to the other pages in the dashboard to see combinations of present-day tribal land belonging to all U.S. tribes, an approximation of the Trail of Tears, and the coordinates that indicate places tribes have been in the past few centuries.
More on this project:
They called it the “Indian problem.” The white settlers wanted more land, and the tribes held rich acreages. Removing tribes from the Southeast was more than just an idea by the time Andrew Jackson was elected president in 1828. The Indian Removal Act was among his defining pieces of legislation. Jackson argued that moving tribes west of the Mississippi River would guarantee their survival.
Instead it launched an era of genocide. Thousands died during the forced marches to land designated as Indian Territory. For members of the 39 tribes in Oklahoma, the removal stories have not been forgotten. Neither has the Dawes Severalty Act of 1887, intended to assimilate Native Americans into white society by stripping them of their cultural and social traditions. The ramifications persist today.
For more, visit the
project site.
Addison Kliewer, Miranda Mahmud and Sarah Beth Guevara are reporters for Gaylord News, a reporting project of the University of Oklahoma Gaylord College of Journalism and Mass Communication. Cronkite News has partnered with OU to expand coverage of indigenous communities.
Note: This story originally appeared on Cronkite News. It is published via a Creative Commons license. Cronkite News is produced by the Walter Cronkite School of Journalism and Mass Communication at Arizona State University.
Search
Filed Under
Tags
More Headlines
Native America Calling: Remembering Ben Nighthorse Campbell and Harvey Pratt
President Trump vetoes tribal homelands bill with swipe at trust relationship
Native America Calling: The Pleiades star cluster ushers in winter story season
NAFOA: 5 Things You Need to Know This Week (January 5, 2026)
Native America Calling: Native in the Spotlight with Elaine Miles
Native America Calling: Gearing yourself up for 2026
Statement: Chairman of Miccosukee Tribe on veto of homelands bill
Native America Calling: Lumbee Nation secures its sovereign status
Chuck Hoskin: Cherokee Nation builds on tradition with technology
Native America Calling: The Year in Native News
Native America Calling: Native music in 2025
Native America Calling: Amid Greenland’s independence push, Denmark accounts for colonial blunders
Senate Committee on Indian Affairs sets business meeting and hearing
Native America Calling: Saving historic architecture and other important places
VIDEO: H.R.2400, the Pit River Land Transfer Act of 2025
More Headlines
President Trump vetoes tribal homelands bill with swipe at trust relationship
Native America Calling: The Pleiades star cluster ushers in winter story season
NAFOA: 5 Things You Need to Know This Week (January 5, 2026)
Native America Calling: Native in the Spotlight with Elaine Miles
Native America Calling: Gearing yourself up for 2026
Statement: Chairman of Miccosukee Tribe on veto of homelands bill
Native America Calling: Lumbee Nation secures its sovereign status
Chuck Hoskin: Cherokee Nation builds on tradition with technology
Native America Calling: The Year in Native News
Native America Calling: Native music in 2025
Native America Calling: Amid Greenland’s independence push, Denmark accounts for colonial blunders
Senate Committee on Indian Affairs sets business meeting and hearing
Native America Calling: Saving historic architecture and other important places
VIDEO: H.R.2400, the Pit River Land Transfer Act of 2025
More Headlines